What Is the Most Expensive Part to Fix on a Furnace?
Furnace repair costs can be a huge concern for homeowners, especially during the colder months when reliable heating is essential. Understanding the potential expenses associated with furnace repairs is crucial for several reasons. It not only helps homeowners budget effectively but also allows them to make informed decisions about maintenance and repair services. In this article, we will delve into the factors that can impact furnace repair costs and discuss why having this knowledge is essential for homeowners.
Key Components in a Typical Furnace:
- Thermostat: The thermostat is the control center of the furnace. It allows homeowners to set the desired temperature for their indoor space. When the temperature falls below the set point, the thermostat signals the furnace to start heating.
- Burner: The burner is responsible for igniting the fuel source, typically natural gas or oil. Once ignited, it produces a flame that heats the air.
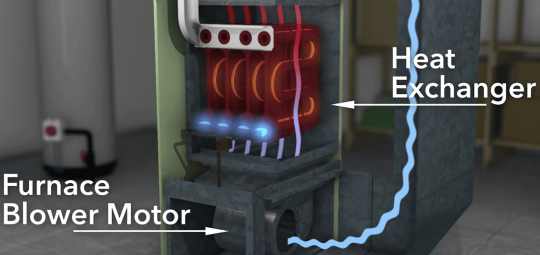
- Heat Exchanger: The heat exchanger is a crucial component that separates the combustion process from the indoor air. It transfers heat from the burner’s flame to the air without mixing the two. This ensures that the indoor air remains free from combustion byproducts.
- Blower Motor: The blower motor is responsible for circulating heated air throughout the ductwork and into the living spaces of the home. It ensures that warm air is evenly distributed, maintaining a comfortable temperature.
- Air Filter: The air filter traps dust, debris, and particles from the incoming air. It plays a vital role in maintaining indoor air quality by preventing contaminants from entering the heating system.
- Ductwork: Ducts are a network of passages that carry heated air from the furnace to various rooms in the house. Properly insulated and sealed ductwork is essential for efficient heating and preventing heat loss.
- Ventilation System: Furnaces have ventilation systems to expel combustion byproducts, such as carbon monoxide, safely out of the home. This ensures the indoor air remains free from harmful gases.

Roles in the Heating Process:
- Thermostat: Initiates the heating process by detecting when the indoor temperature drops below the desired setting.
- Burner: Combusts fuel to produce heat energy.
- Heat Exchanger: Transfers heat from the burner to the air without allowing combustion byproducts to mix with indoor air.
- Blower Motor: Circulates heated air throughout the home to maintain a consistent temperature.
- Air Filter: Improves indoor air quality by capturing particles and allergens, ensuring clean, warm air is distributed.
- Ductwork: Distributes heated air to various rooms in the house, ensuring even heating.
- Ventilation System: Safely vents combustion byproducts to the outside, maintaining indoor air quality and safety.
Understanding these components and their roles is essential for homeowners to know how their furnace functions and to identify potential issues that may require maintenance or repair.
Common Issues Homeowners May Encounter with Their Furnaces:
- Clogged Air Filters: Over time, air filters in furnaces can become clogged with dust, debris, and allergens. This reduces airflow, making the furnace work harder and less efficiently. Clogged filters are a common issue and are relatively inexpensive to replace or clean.
- Ignition or Pilot Problems: Furnaces that use gas require a functioning ignition or pilot light to start the heating process. Issues with ignition components can vary in complexity, from a simple pilot light adjustment to more extensive repairs, impacting repair costs accordingly.
- Thermostat Malfunctions: A malfunctioning thermostat can lead to inaccurate temperature readings or failure to signal the furnace to turn on when needed. Thermostat repairs or replacements can vary in cost depending on the model and complexity.
- Blower Motor Problems: The blower motor is responsible for distributing heated air. Issues with the blower motor can lead to uneven heating or a lack of warm air circulation. Repair costs for the blower motor can range from minor adjustments to motor replacement.
- Dirty or Faulty Flame Sensors: Flame sensors in gas furnaces detect the presence of a flame. If they become dirty or malfunction, the furnace may not ignite or may shut down prematurely. Cleaning or replacing a flame sensor is usually a relatively affordable repair.
- Ductwork Leaks: Leaky ducts can cause heat loss, reducing the efficiency of the furnace. The cost to repair ductwork can vary significantly based on the extent of the damage and accessibility within the home.
- Cracked Heat Exchanger: A cracked heat exchanger can be a serious issue, as it can lead to carbon monoxide leaks. Repairing or replacing a heat exchanger is a major and costly repair, often requiring professional expertise.
- Frequent Cycling: If the furnace turns on and off frequently, it can indicate a problem with the thermostat, airflow, or other components. Repair costs depend on identifying and addressing the root cause of this issue.
- Unusual Noises: Unusual noises like rattling, banging, or squealing can signal various problems, such as loose parts or damaged components. The cost of repairs depends on diagnosing and addressing the specific issue.
- Lack of Maintenance: Neglecting regular maintenance can lead to a host of problems in the long run, potentially resulting in higher repair costs. Routine maintenance can help prevent many common furnace issues.
Note: that the repair costs for these furnace problems can vary widely, ranging from minor adjustments or filter replacements that are relatively affordable to more complex issues like heat exchanger replacements, which can be costly. Regular maintenance and prompt attention to furnace issues can help homeowners minimize repair expenses and ensure their heating system operates efficiently.
What is the most expensive part to fix on a furnace?
The Most Expensive Furnace Component: The Heat Exchanger
The specific furnace component that is typically the most expensive to repair or replace is the heat exchanger.

Reasons behind its high cost:
- Complexity of Manufacturing: Heat exchangers are intricate components made from high-quality materials. They must withstand extreme temperatures and pressure differentials, which requires precision engineering and manufacturing. The complexity of producing a durable and efficient heat exchanger contributes to its high cost.
- Safety Concerns: Heat exchangers play a critical role in separating the combustion process from indoor air. A cracked or faulty heat exchanger can lead to carbon monoxide leaks, posing a severe safety hazard. Due to the potential risks associated with heat exchanger issues, replacement or repair must meet stringent safety standards, adding to the overall cost.
- Labor Intensity: Replacing or repairing a heat exchanger is a labor-intensive task that often requires the disassembly and reassembly of various furnace components. HVAC professionals need specialized training and equipment to perform this task safely and effectively, which adds to the labor costs.
- Parts and Materials: Heat exchangers are typically constructed from high-grade stainless steel or other heat-resistant alloys. These materials can be expensive to source and work with, contributing to the overall cost of repair or replacement.
- Diagnostic Efforts: Diagnosing a heat exchanger issue often requires a thorough inspection and testing of the furnace. This process may involve advanced diagnostic tools and expertise, which can increase the overall service cost.
- Manufacturer Warranty: Many heat exchangers come with warranties that cover replacements if they fail within a certain timeframe. However, these warranties may not cover labor costs or may have limitations, leaving homeowners responsible for a significant portion of the expenses.
- Permit Requirements: In some areas, replacing a heat exchanger may require obtaining permits and complying with local building codes, which can add administrative and inspection costs.
Due to the combination of safety concerns, labor-intensive processes, specialized materials, and potential warranty limitations, repairing or replacing a heat exchanger is one of the costliest furnace repairs. Homeowners should prioritize regular maintenance and promptly address any furnace issues to avoid the need for such expensive repairs. Contact us for a furnace checkup before winter hits!
Read the full article
Comments
Post a Comment